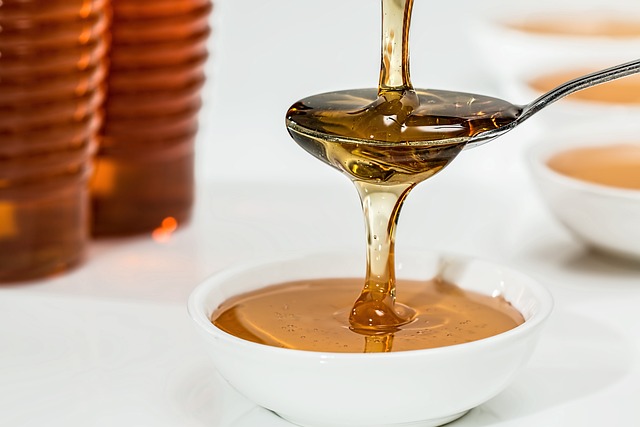
Introduction: What is Diabetes and How Does Honey Affect it?
The sweetener has been used as a folk remedy for centuries, and while there is some scientific evidence to support its use, honey should be used with caution by people with diabetes.
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the body’s ability to process blood sugar (glucose). There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2. Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in childhood, while type 2 diabetes typically develops in adulthood.
Honey has been shown to have potential benefits for both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. In general, honey may help lower blood sugar levels by increasing insulin sensitivity and reducing inflammation. Additionally, research suggests that honey may also help improve cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease in people with diabetes.
While honey may offer some health benefits for people with diabetes, it’s important to remember that it is still a form of sugar. As such, it should be used in moderation and not used as a substitute for other forms of treatment. People with diabetes should work closely with their healthcare team to create an individualized treatment plan that includes diet, exercise, and medication.
Pros of Eating Honey for Diabetics
Honey has been used as a natural sweetener for centuries and is gaining popularity as a health food. While honey does contain sugar, it also has a lower glycemic index than table sugar and may help to regulate blood sugar levels. For people with diabetes, honey may provide several potential benefits.
- Honey May Help Control Blood Sugar Levels
Studies have shown that honey can help to control blood sugar levels in people with diabetes. In one study, participants who ate honey before bed had lower fasting blood sugar levels in the morning than those who did not eat honey (1).
Another study found that consuming honey prior to exercise helped to maintain blood sugar levels during and after exercise in people with type 1 diabetes (2). This effect was attributed to the fact that honey contains both glucose and fructose, which are absorbed at different rates and help to keep blood sugar levels stable.
- Honey May Have Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Honey contains compounds like phenols and flavonoids that have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects (3). These properties may help to reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes, such as heart disease and nerve damage.
- Honey May Boost Energy Levels and Aid in Weight Loss
Honey has been shown to increase energy levels and aid in weight loss when used in place of other sweeteners (4, 5). This is likely due to the fact that honey contains less fructose than other sweet
Cons of Eating Honey for Diabetics
Although honey has many benefits, there are also some drawbacks to consider if you have diabetes. One of the main cons is that honey can cause blood sugar spikes. This is because honey is high in fructose, which can cause your blood sugar to rise quickly. If you are trying to keep your blood sugar levels under control, eating honey may not be the best option. Another downside to eating honey is that it can contain harmful bacteria. This is especially true if you eat raw or unpasteurized honey. These types of honey can contain botulism spores, which can be dangerous for people with diabetes. Finally, honey is high in calories and carbohydrates. If you are trying to lose weight or manage your diabetes, eating honey may not be the best choice.
Different Types of Honey and their Effects on Blood Sugar Levels
There are different types of honey and each type has a different effect on blood sugar levels. The two main types of honey are raw honey and processed honey. Raw honey is made from the nectar of flowers and has not been heated or processed. This type of honey still contains pollen, enzymes, and minerals which can help regulate blood sugar levels. Processed honey is made from the nectar of flowers but has been heated and filtered. This process removes the pollen, enzymes, and minerals from the honey which can cause blood sugar levels to spike.
Raw honey has a lower glycemic index than processed honey which means it doesn’t cause blood sugar levels to spike as much. Raw honey also contains antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals which can help improve overall health. Processed honey may be easier to find in stores but raw honey is definitely the better choice for diabetics.
Natural Sweeteners to Consider instead of Honey
There are a few natural sweeteners to consider instead of honey if you are diabetic. One is stevia, which comes from the leaves of the plant species Stevia rebaudiana. The other is monk fruit, which comes from the siraitia grosvenorii plant. Both of these sweeteners are safe for diabetics and do not raise blood sugar levels.
Recommendations and Tips for Eating Honey with Diabetes
If you have diabetes, you may think that honey is off-limits. But the truth is, honey can be a part of a healthy diet for people with diabetes. Here are some recommendations and tips for eating honey with diabetes:
- Choose raw, unfiltered honey. Raw honey contains more nutrients and antioxidants than processed honey.
- Use honey in moderation. Even though honey is a natural sweetener, it still contains calories and carbohydrates. So, it’s important to use it in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
- Add honey to your diet slowly. If you’re not used to eating honey, start by adding a small amount to your diet and gradually increase the amount you eat over time.
- Monitor your blood sugar levels closely when you start eating honey. As with any new food, it’s important to monitor your blood sugar levels closely when you first start incorporating honey into your diet to make sure it doesn’t cause any spikes or dips in your blood sugar levels.
- Talk to your doctor or registered dietitian about whether or not honey is right for you and what the best way to incorporate it into your diet is. As with any changes to your diet, it’s always best to talk to your doctor or registered dietitian first before making any changes on your own.
Conclusion
Although the jury is still out on whether honey is safe for people with diabetes, it certainly shows promise. Studies have suggested that consuming raw honey in small doses can help regulate blood sugar levels and provide essential vitamins and minerals to support overall health. Ultimately, however, diabetics should consult their medical practitioner before adding any new food item to their diet and always monitor their glucose levels closely when introducing something new. With all this in mind, we hope that you now feel better informed about the potential benefits of honey for diabetics.